Kinova Robotics
Kinova Robotics designs and manufactures service robots for the most discriminating end user – human beings. With years of experience, they offer the skills and engineering expertise needed for such a demanding task. Taking advantage of the latest technologies, Kinova continually advances their service robots, creating higher quality and more useable products. This article discusses how Kinova utilized flat brushless motors for service robots they created to help disabled individuals perform daily tasks.
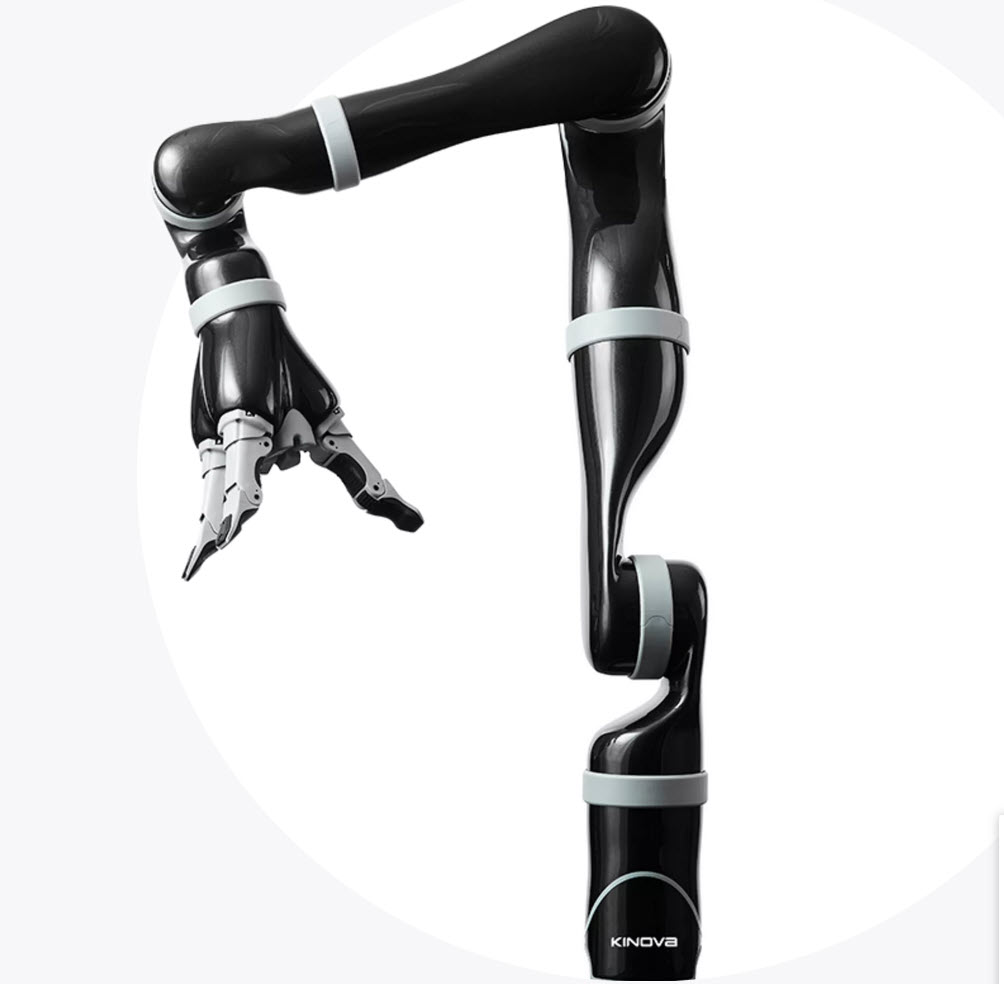
Jaco2 Robotic Arm
The Jaco2 Robotic Arm is a lightweight, quiet, easily controlled service device created to help disabled individuals with daily tasks. The arm moves around 6 degrees of freedom using 6 flat motors designed and manufactured by maxon precision motors. With 6 joints ranging from a shoulder-type joint to a functional wrist, the arm can handle 1.5 kg payload at full extension and 2.5 kg payload at mid-range extension; These capabilities are adequate to meet the needs of most disabled people in daily life.
Weighing only 5.3 kg overall, the device can be mounted to a wheelchair without the risk of tipping it over. To maintain this crucial lightweight design, the device used a lightweight and efficient flat motor series from maxon.
The Role of maxon motors – Brushless DC Motors for Service Robots
The first three joints of the device are those that handle the highest torque for movement of the extended arm as well as for lifting items. Here, Kinova’s team chose to use maxon’s EC 45 flat brushless DC motors. These motors pack a maximum continuous torque of up to 134 mNm in a small, compact 70 Watt package. The EC motors also produced less heat, which is crucial since the Jaco2 needed to fit within the robotic arm itself. Although EC 45 motors can operate at a very high speed, this was not a requirement for this specific application.
The second three joints also used EC 45 flat motors, but the 30 Watt versions, again chosen for their ability to keep heat dissipation low and for their compact size. Maxon also allowed slight customizations, which enabled the Kinova team to fit the motors perfectly within the device. The arm uses Harmonic Drive gears translating to a 1:136 ratio for the large actuators in joints one and three, a 1:160 ratio for the large actuators in joint two, and 1:110 for the small actuators in joints four, five, and six.
For the finger of the robot, Kinova utilized three of maxon’s EC32 15 Watt motors. Kinova decided to design the linear actuators in-house due to it being more expensive to purchase them from a vendor. Although the flat motors did have some degree of cogging, it did not affect the accuracy or other operations of Jaco2 that would be crucial to the user. Yet another crucial feature that led to the use of maxon motors was their quiet operation; this helped Kinova reach their goal of making the device as transparent as possible to the end user.
All motors are daisy-chained together using one cable that runs through the system. Each arm can be easily controlled through the user’s wheelchair control or through a joystick, providing precise operation. The software for the device runs on Windows, Linux Ubuntu, and ROS and was written using C# and C++.
For more information regarding the maxon motors used in this application or harmonic drive gears, contact Electromate today.